Monday, October 4, 2021 – Stained Glass
- Mary Reed

- Oct 4, 2021
- 20 min read
Updated: Oct 6, 2021
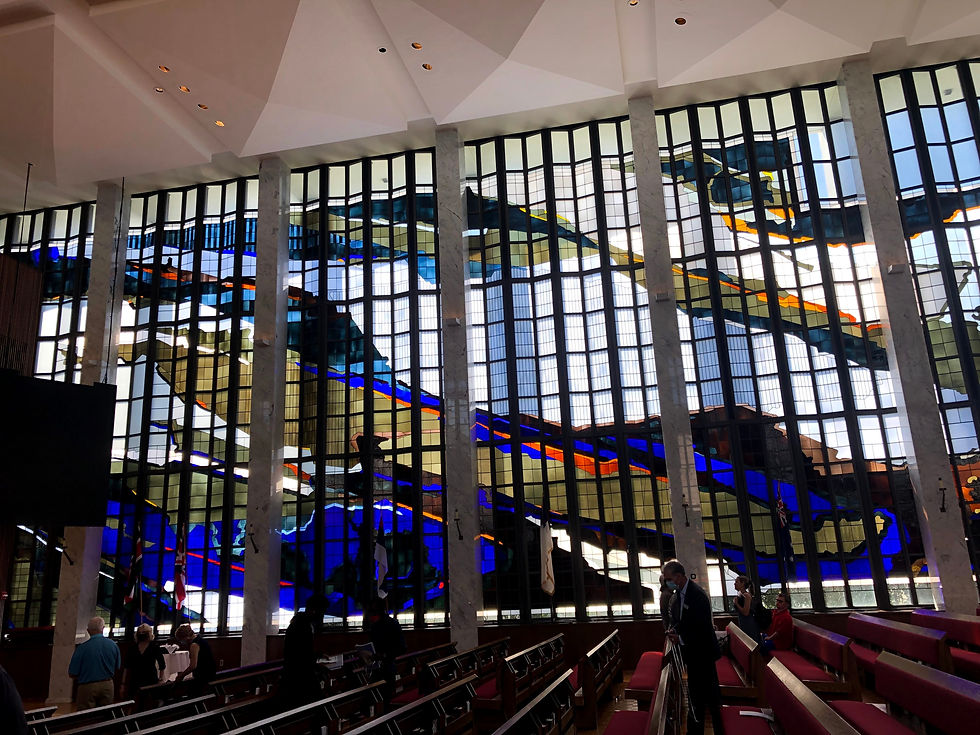

The photo is of some of the stained-glass windows at my church, Lovers Lane United Methodist in Dallas. It has been described as a stunning architectural gem, its soaring glass walls and 36-foot ceiling making it the largest freestanding stained-glass structure in North America. It is quite overpowering and humbling to be surrounded by the majesty of the stained glass. Really does make you feel like you are in the presence of something greater than you are, something that can touch your soul and pluck your heartstrings. The vastness of the windows exudes spirituality and wisdom. I have always loved stained glass. The way light filters through it surely can set a mood. Stained glass can be huge like the windows or tiny like miniature lamps. There is often exquisite artistry in stained glass. To be the creator of such beauty must be a transcendent experience. Let’s learn more about stained glass.
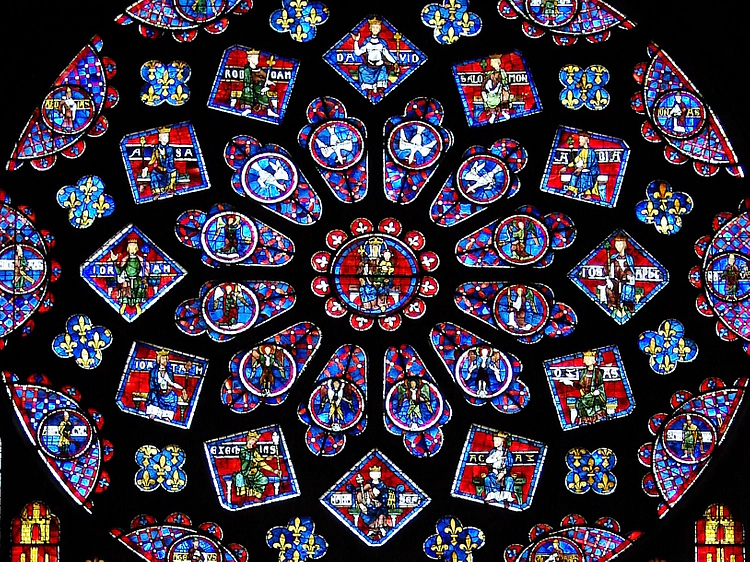

According to Wikipedia, the term stained-glass refers to colored glass as a material and the works created from it. Throughout its thousand-year history, the term has been applied almost exclusively to the windows of churches and other significant religious buildings. Although traditionally made in flat panels and used as windows, the creations of modern stained glass artists also include three-dimensional structures and sculpture. Modern vernacular usage has often extended the term "stained glass" to include domestic lead light and objets d'art created from foil glasswork exemplified in the famous lamps of Louis Comfort Tiffany.
As a material stained glass is glass that has been colored by adding metallic salts during its manufacture, and usually then further decorating it in various ways. The colored glass is crafted into stained glass windows in which small pieces of glass are arranged to form patterns or pictures, traditionally held together by strips of lead and supported by a rigid frame. Painted details and yellow stain are often used to enhance the design. The term stained glass is also applied to windows in enameled glass in which the colors have been painted onto the glass and then fused to the glass in a kiln; very often this technique is only applied to parts of a window.
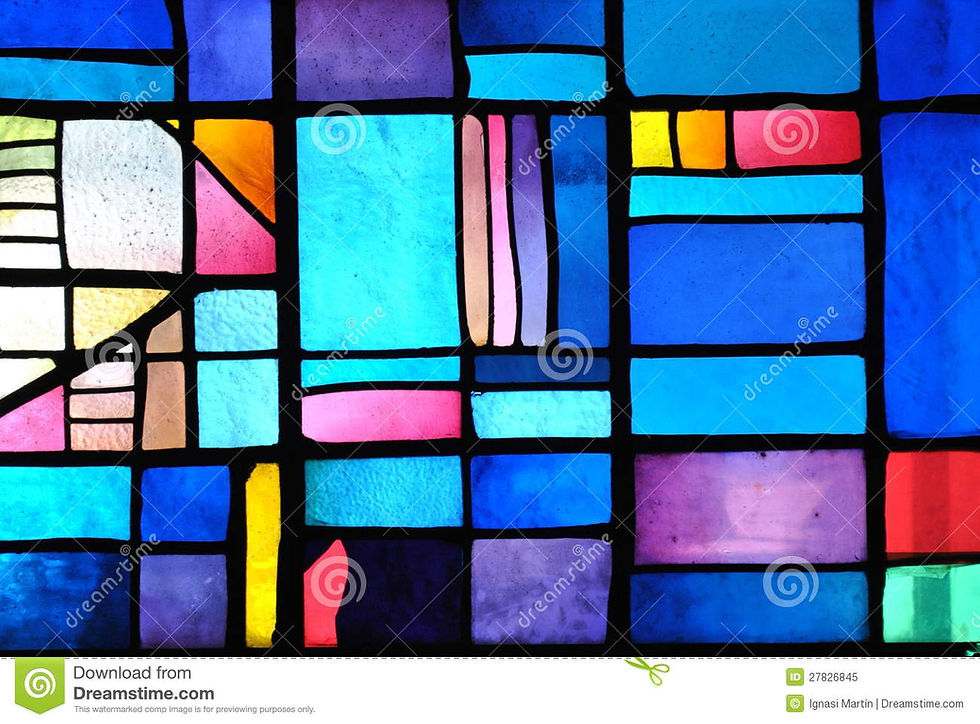

Stained glass, as an art and a craft, requires the artistic skill to conceive an appropriate and workable design and the engineering skills to assemble the piece. A window must fit snugly into the space for which it is made, must resist wind and rain, and also — especially in the larger windows — must support its own weight. Many large windows have withstood the test of time and remained substantially intact since the Late Middle Ages. In Western Europe, together with illuminated manuscripts, they constitute the major form of medieval pictorial art to have survived. In this context, the purpose of a stained-glass window is not to allow those within a building to see the world outside or even primarily to admit light but rather to control it. For this reason, stained-glass windows have been described as "illuminated wall decorations."
The design of a window may be abstract or figurative; may incorporate narratives drawn from the Bible, history or literature; may represent saints or patrons, or use symbolic motifs, in particular bearing a coat of arms. Windows within a building may be thematic, for example: within a church — episodes from the life of Christ, within a parliament building — shields of the constituencies, within a college hall — figures representing the arts and sciences or within a home — flora, fauna or landscape.

Glass production
During the late medieval period, glass factories were set up where there was a ready supply of silica, the essential material for glass manufacture. Silica requires a very high temperature to melt, something not all glass factories were able to achieve. Such materials as potash, soda and lead can be added to lower the melting temperature. Other substances, such as lime, are added to rebuild the weakened network and make the glass more stable. Glass is colored by adding metallic oxide powders or finely divided metals while it is in a molten state. Copper oxides produce green or bluish green, cobalt makes deep blue and gold produces wine red and violet glass. Much of modern red glass is produced using copper, which is less expensive than gold and gives a brighter, more vermilion shade of red. Glass colored while in the clay pot in the furnace is known as pot metal glass, as opposed to flashed glass.
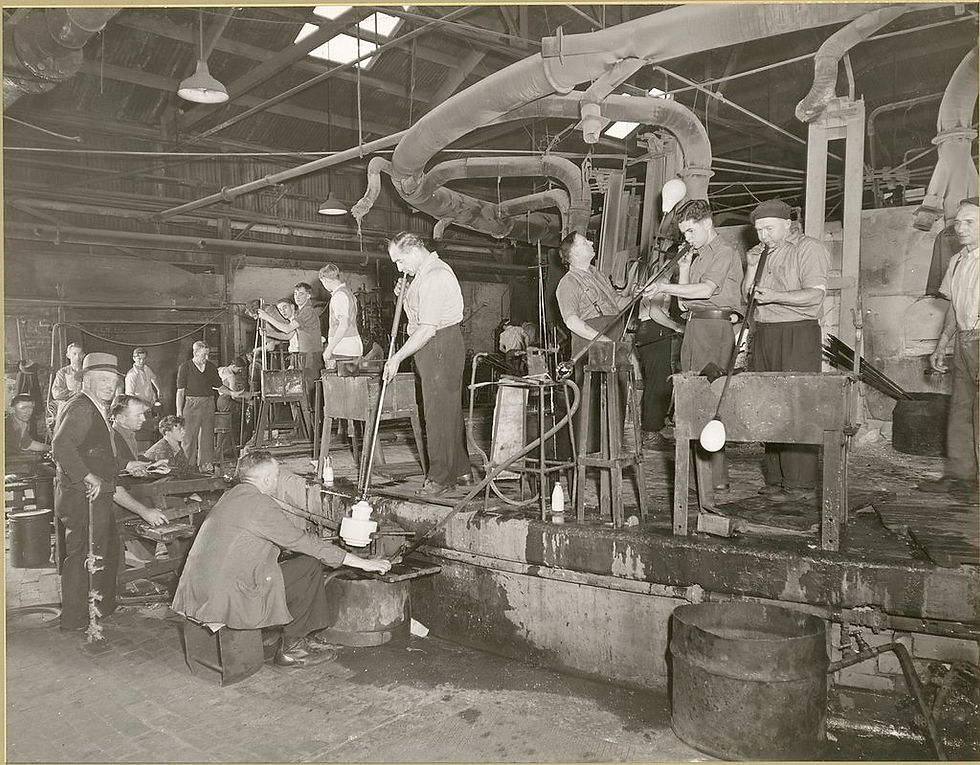

Cylinder glass or muff glass
Using a blowpipe, a "gather" or glob of molten glass is taken from the pot heating in the furnace. The gather is formed to the correct shape and a bubble of air blown into it. Using metal tools, molds of wood that have been soaking in water and gravity, the gather is manipulated to form a long, cylindrical shape. As it cools, it is reheated so that the manipulation can continue. During the process, the bottom of the cylinder is removed. Once brought to the desired size it is left to cool. One side of the cylinder is opened. It is put into another oven to quickly heat and flatten it, and then placed in an annealer to cool at a controlled rate, making the material more stable. "Hand-blown" cylinder — also called muff glass — and crown glass were the types used in ancient stained-glass windows. Stained glass windows were normally in churches and chapels, as well as many more well-respected buildings.
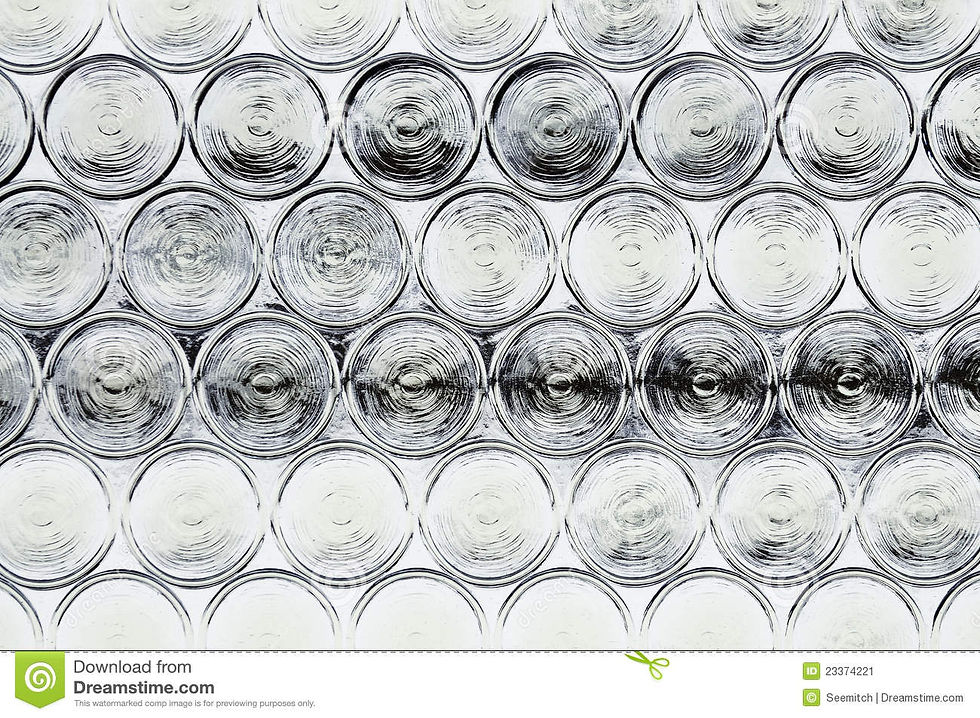

Crown glass
This hand-blown glass is created by blowing a bubble of air into a gather of molten glass and then spinning it, either by hand or on a table that revolves rapidly like a potter's wheel. The centrifugal force causes the molten bubble to open up and flatten. It can then be cut into small sheets. Glass formed this way can be either colored and used for stained-glass windows, or uncolored as seen in small paned windows in 16th- and 17th-century houses. Concentric, curving waves are characteristic of the process. The center of each piece of glass — known as the "bull's-eye" — is subject to less acceleration during spinning, so it remains thicker than the rest of the sheet. It also has the pontil mark, a distinctive lump of glass left by the "pontil" rod, which holds the glass as it is spun out. This lumpy, refractive quality means the bulls’ eyes are less transparent, but they still have been used for windows, both domestic and ecclesiastical. Crown glass is still made today, but not on a large scale

Rolled glass
Rolled glass — sometimes called "table glass" — is produced by pouring molten glass onto a metal or graphite table and immediately rolling it into a sheet using a large metal cylinder, similar to rolling out a pie crust. The rolling can be done by hand or by machine. Glass can be "double rolled" which means it is passed through two cylinders at once — similar to the clothes wringers on older washing machines — to yield glass of a specified thickness, typically about 1/8-inch. The glass is then annealed. Rolled glass was first commercially produced around the mid-1830s and is widely used today. It is often called cathedral glass, but this has nothing to do with medieval cathedrals, where the glass used was hand-blown.
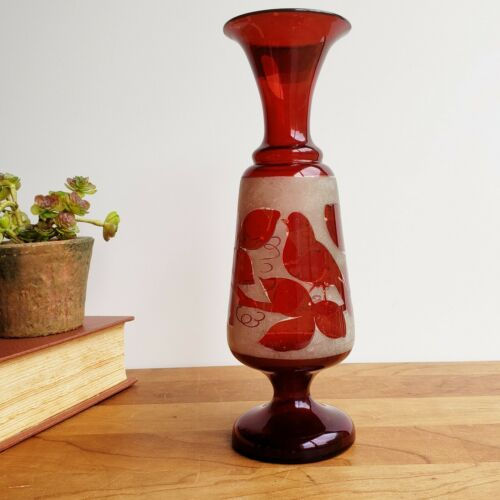

Flashed glass
Architectural glass must be at least 1/8-inch thick to survive the push and pull of typical wind loads. However, in the creation of red glass, the coloring ingredients must be of a certain concentration, or the color will not develop. This results in a color so intense that at the thickness of 1/8-inch, the red glass transmits little light and appears black. The method employed is to laminate a thin layer of red glass to a thicker body of glass that is clear or lightly tinted, forming "flashed glass."
A lightly colored molten gather is dipped into a pot of molten red glass, which is then blown into a sheet of laminated glass using either the cylinder/muff or the crown technique described above. Once this method was found for making red glass, other colors were made this way as well. A great advantage is that the double-layered glass can be engraved or abraded to reveal the clear or tinted glass below. The method allows rich detailing and patterns to be achieved without needing to add more lead-lines, giving artists greater freedom in their designs. A number of artists have embraced the possibilities flashed glass gives them. For instance, 16th-century heraldic windows relied heavily on a variety of flashed colors for their intricate crests and creatures. In the medieval period the glass was abraded; later, hydrofluoric acid was used to remove the flash in a chemical reaction — a very dangerous technique, and in the 19th century sandblasting started to be used for this purpose.

Modern production of traditional glass
There are a number of glass factories, notably in Germany, the United States, England, France, Poland and Russia, which produce high-quality glass, both hand-blown (cylinder, muff, crown) and rolled (cathedral and opalescent). Modern stained-glass artists have many resources to use and the work of centuries of other artists from which to learn as they continue the tradition in new ways. In the late 19th and 20th centuries there have been many innovations in techniques and in the types of glass used. Many new types of glass have been developed for use in stained glass windows, in particular Tiffany glass and Dalle de verre.
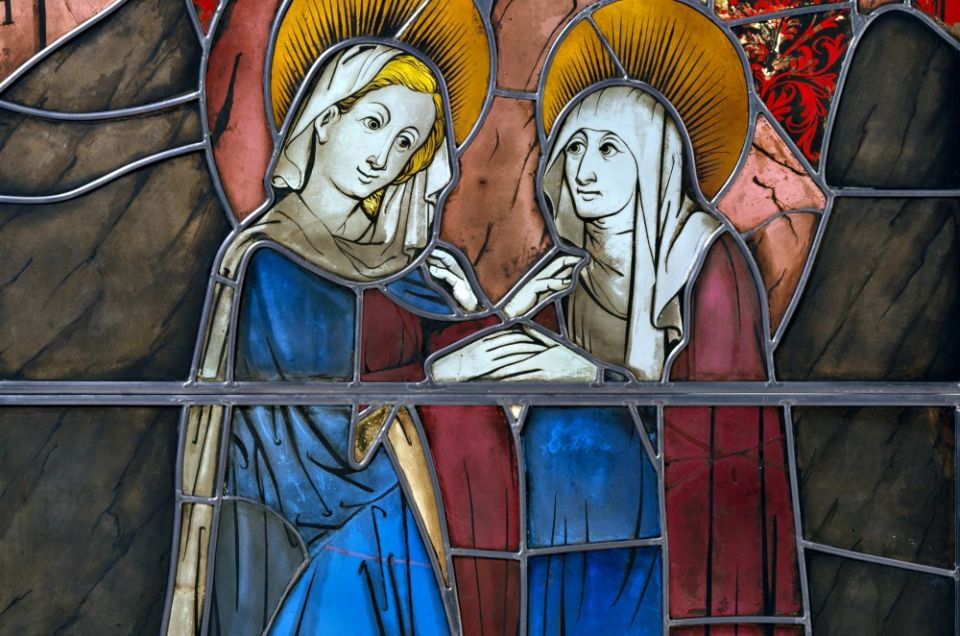

“Pot metal” and flashed glass
The primary method of including color in stained glass is to use glass — originally colorless — that has been given coloring by mixing with metal oxides in its melted state in a crucible or "pot," producing glass sheets that are colored all the way through; these are known as "pot metal" glass. A second method, sometimes used in some areas of windows, is flashed glass, a thin coating of colored glass fused to colorless glass or colored glass, to produce a different color. In medieval glass, flashing was especially used for reds, as glass made with gold compounds was very expensive and tended to be too deep in color to use at full thickness. In the photo of “The Visitation,” pot metal of various colors are used, including white glass, black vitreous paint and yellow silver stain.
Glass Paint
Another group of techniques give additional coloring, including lines and shading, by treating the surfaces of the colored sheets, and often fixing these effects by a light firing in a furnace or kiln. These methods may be used over broad areas, especially with silver stain, which gave better yellows than other methods in the Middle Ages. Alternatively, they may be used for painting linear effects or polychrome areas of detail. The most common method of adding the black linear painting necessary to define stained glass images is the use of what is variously called "glass paint," "vitreous paint" or "grisaille paint." It was applied as a mixture of powdered glass, iron or rust filings to give a black color and clay and oil, vinegar or water for a brushable texture, with a binder such as gum arabic. This was painted on the pieces of colored glass, and then fired to burn away the ingredients giving texture, leaving a layer of the glass and coloring fused to the main glass piece.
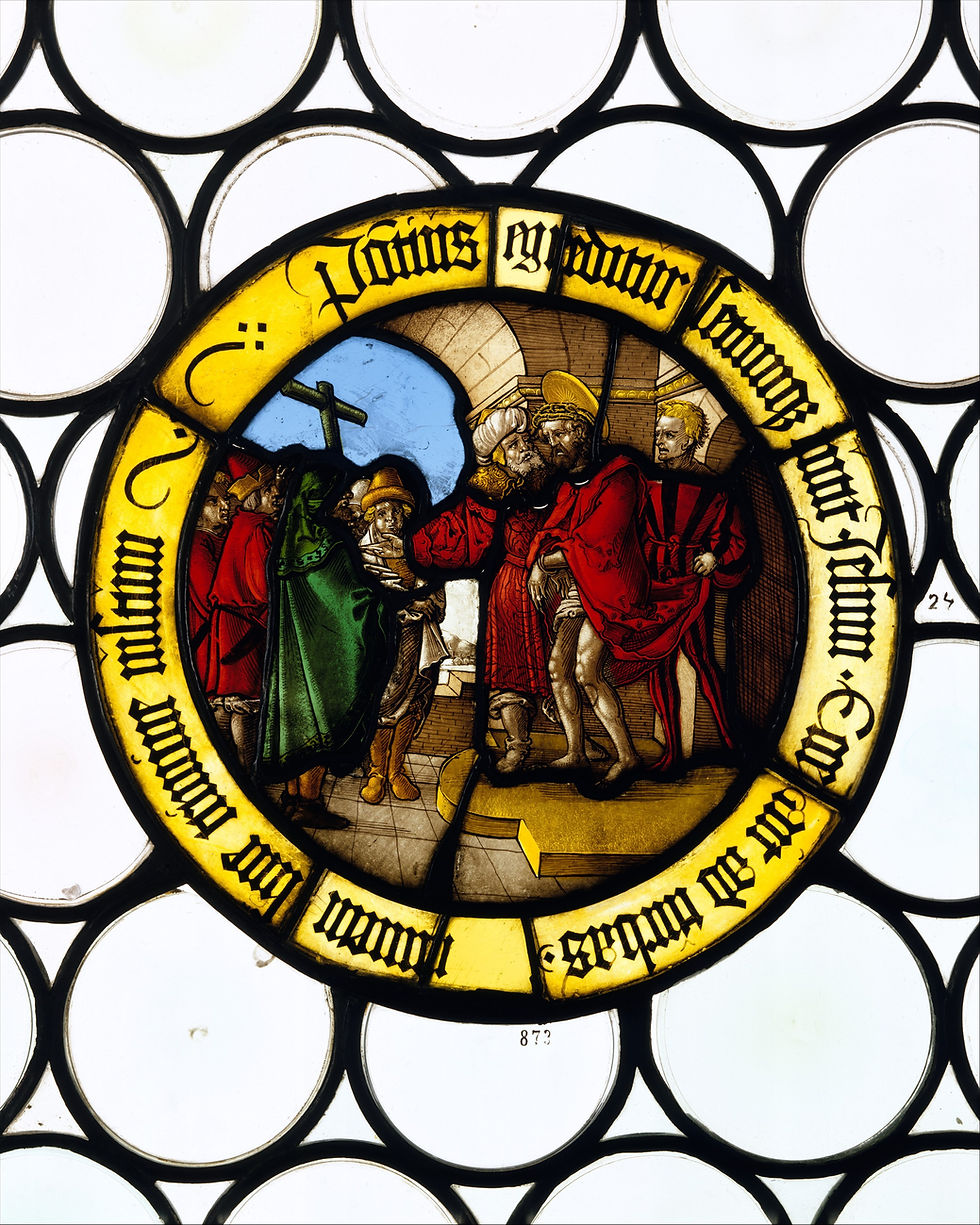

Silver stain
"Silver stain," introduced soon after 1300, produced a wide range of yellow to orange colors; this is the "stain" in the term "stained glass." Silver compounds — notably silver nitrate — are mixed with binding substances, applied to the surface of glass and then fired in a furnace or kiln. They can produce a range of colors from orange-red to yellow. Used on blue glass they produce greens. The way the glass is heated and cooled can significantly affect the colors produced by these compounds. The chemistry involved is complex and not well understood. The chemicals actually penetrate the glass they are added to a little way, and the technique therefore gives extremely stable results. By the 15th century it had become cheaper than using pot metal glass and was often used with glass paint as the only color on transparent glass. Silver stain was applied to the opposite face of the glass to silver paint, as the two techniques did not work well one on top of the other. The stain was usually on the exterior face, where it appears to have given the glass some protection against weathering, although this can also be true for paint. They were also probably fired separately, the stain needing a lower heat than the paint. In the photo above of “Nuremburg,” silver stain painted on the reverse of the blue sky gives the dark green of the cross.
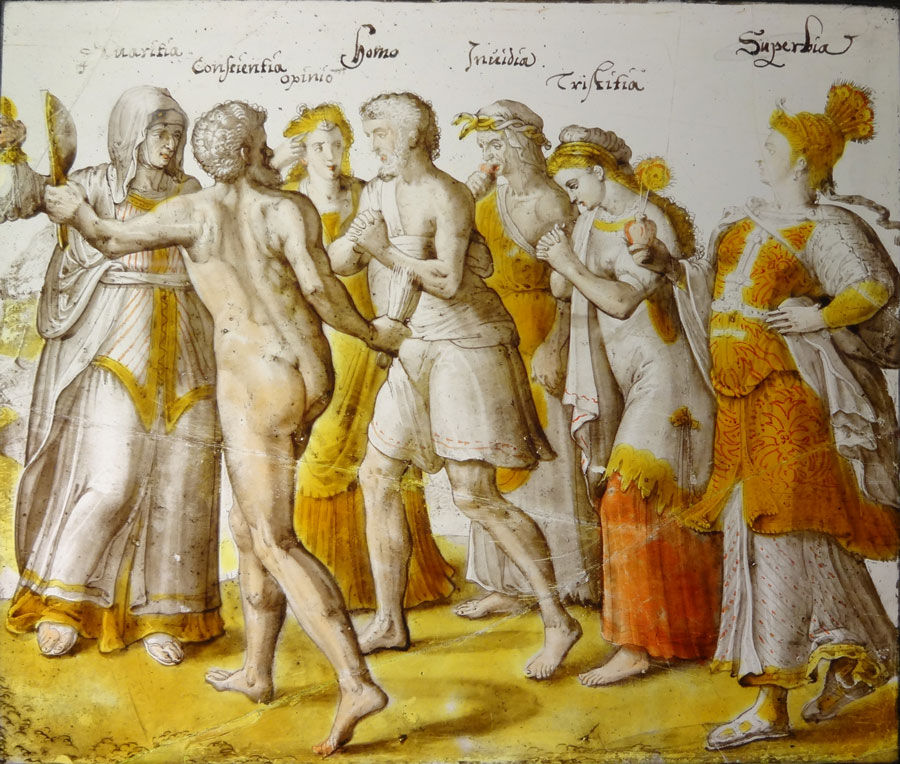

“Sanguine” or “Cousin’s rose”
"Sanguine," "carnation," "Rouge Jean Cousin" or "Cousin's rose" — after its supposed inventor Jean Cousin — is an iron-based fired paint producing red colors, mainly used to highlight small areas, often on flesh. It was introduced around 1500. In the photo on the left the young woman with clasped hands and bowed head is Tristitia or Melancholy. Her lower skirt is painted with sanguine to give it a redder color. The bearded naked man with his back to us is Conscientia or Conscience. His body is painted with carnation to give a good flesh tone. The figure to the far right is Superbia or Pride. Carnation was also used to paint the pattern on the clothing. Copper stain — similar to silver stain but using copper compounds, also produced reds — and was mainly used in the 18th and 19th centuries.
Cold paint
"Cold paint" is various types of paint that were applied without firing. Contrary to the optimistic claims of the 12th century writer Theophilus Presbyter, cold paint is not very durable and very little medieval paint has survived.

Scratching techniques
As well as painting, scratched sgraffito techniques were often used. It involved painting a color over pot metal glass of another color, and then before firing, selectively scratching the glass paint away to make the design or the lettering of an inscription. It was the most common method of making inscriptions in early medieval glass, giving white or light letters on a black background, with later inscriptions more often using black painted letters on a transparent glass background.

Design of stained-glass windows
The first stage in the production of a window is to make or acquire from the architect or owners of the building an accurate template of the window opening that the glass is to fit.
The subject matter of the window is determined to suit the location, a particular theme or the wishes of the patron. A small design called a Vidimus from Latin "we have seen" is prepared which can be shown to the patron. A scaled model maquette may also be provided. The designer must take into account the design, the structure of the window, the nature and size of the glass available and his or her own preferred technique.
A traditional narrative window has panels which relate a story. A figurative window could have rows of saints or dignitaries. Scriptural texts or mottos are sometimes included and perhaps the names of the patrons or the person to whose memory the window is dedicated. In a window of a traditional type, it is usually left to the discretion of the designer to fill the surrounding areas with borders, floral motifs and canopies.
A full-sized cartoon is drawn for every "light" or opening of the window. A small church window might typically have two lights, with some simple tracery lights above. A large window might have four or five lights. The east or west window of a large cathedral might have seven lights in three tiers, with elaborate tracery. In medieval times the cartoon was drawn directly on the surface of a whitewashed table, which was then used as a pattern for cutting, painting and assembling the window. The cartoon is then divided into a patchwork, providing a template for each small glass piece. The exact position of the lead which holds the glass in place is also noted, as it is part of the calculated visual effect.
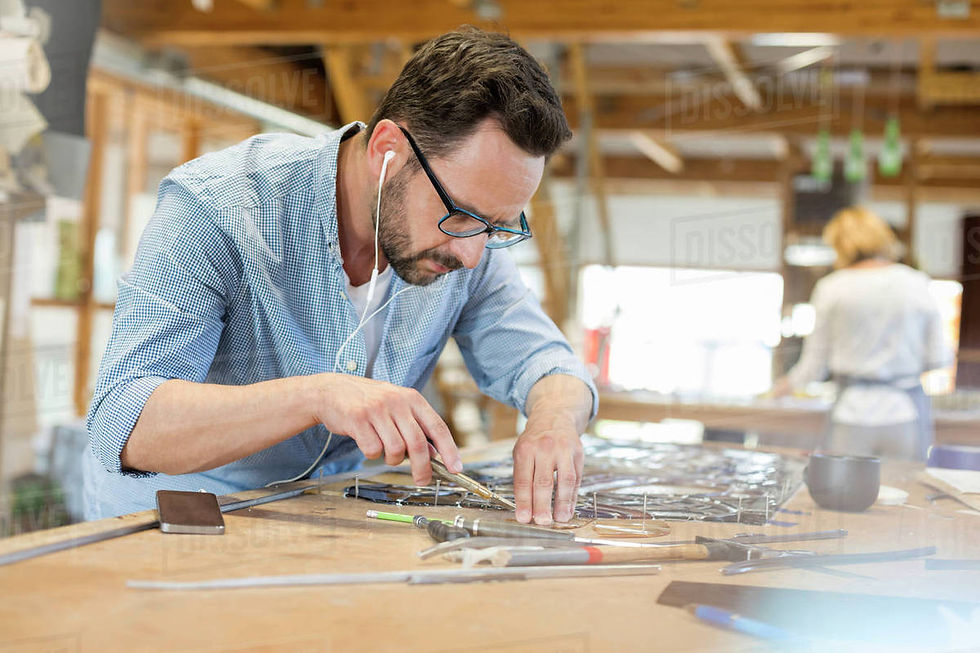

Selecting and painting the glass
Each piece of glass is selected for the desired color and cut to match a section of the template. An exact fit is ensured by "grozing" the edges with a tool which can nibble off small pieces. Details of faces, hair and hands can be painted onto the inner surface of the glass using a special glass paint which contains finely ground lead or copper filings, ground glass, gum arabic and a medium such as wine, vinegar or traditionally urine. The art of painting details became increasingly elaborate and reached its height in the early 20th century.
From 1300 onwards, artists started using "silver stain" which was made with silver nitrate. It gave a yellow effect ranging from pale lemon to deep orange. It was usually painted onto the outside of a piece of glass, then fired to make it permanent. This yellow was particularly useful for enhancing borders, canopies and halos, and turning blue glass into green glass. By about 1450, a stain known as "Cousin's rose" was used to enhance flesh tones.
In the 16th century, a range of glass stains were introduced, most of them colored by ground glass particles. They were a form of enameled glass. Painting on glass with these stains was initially used for small heraldic designs and other details. By the 17th century a style of stained glass had evolved that was no longer dependent upon the skillful cutting of colored glass into sections. Scenes were painted onto glass panels of square format, like tiles. The colors were then annealed to the glass before the pieces were assembled.
A method used for embellishment and gilding is the decoration of one side of each of two pieces of thin glass, which are then placed back-to-back within the lead came or divider bar. This allows for the use of techniques such as Angel gilding and Eglomise to produce an effect visible from both sides but not exposing the decorated surface to the atmosphere or mechanical damage.
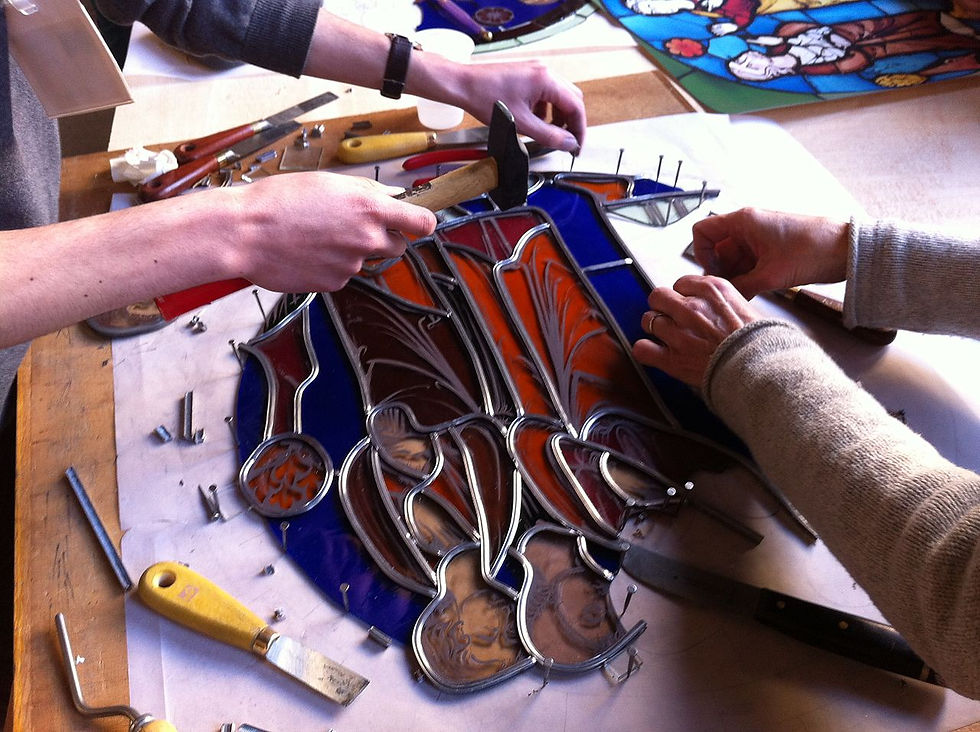

Assembly and mounting
Once the glass is cut and painted, the pieces are assembled by slotting them into H-sectioned lead cames. All the joints are then soldered together, and the glass pieces are prevented from rattling and the window made weatherproof by forcing a soft oily cement or mastic between the glass and the cames. In modern windows, copper foil is now sometimes used instead of lead.
Traditionally, when a window was inserted into the window space, iron rods were put across it at various points to support its weight. The window was tied to these rods with copper wire. Some very large early Gothic windows are divided into sections by heavy metal frames called ferramenta. This method of support was also favored for large, usually painted, windows of the Baroque period.

Historical origins
Colored glass has been produced since ancient times. Both the Egyptians and the Romans exceled at the manufacture of small colored glass objects. Phoenicia was important in glass manufacture with its chief centers Sidon, Tyre and Antioch. The British Museum holds two of the finest Roman pieces — the Lycurgus Cup, which is a murky mustard color but glows purple-red to transmitted light and the cameo glass Portland vase which is midnight blue with a carved white overlay.
In early Christian churches of the 4th and 5th centuries, there are many remaining windows which are filled with ornate patterns of thinly sliced alabaster set into wooden frames, giving a stained-glass like effect.
Evidence of stained-glass windows in churches and monasteries in Britain can be found as early as the 7th century. The earliest known reference dates from 675 AD when Benedict Biscop imported workmen from France to glaze the windows of the monastery of St. Peter which he was building at Monkwearmouth. Hundreds of pieces of colored glass and lead — dating back to the late 7th century — have been discovered there and at Jarrow.
In the Middle East, the glass industry of Syria continued during the Islamic period with major centers of manufacture at Raqqa, Aleppo and Damascus and the most important products being highly transparent colorless glass and gilded glass, rather than colored glass.
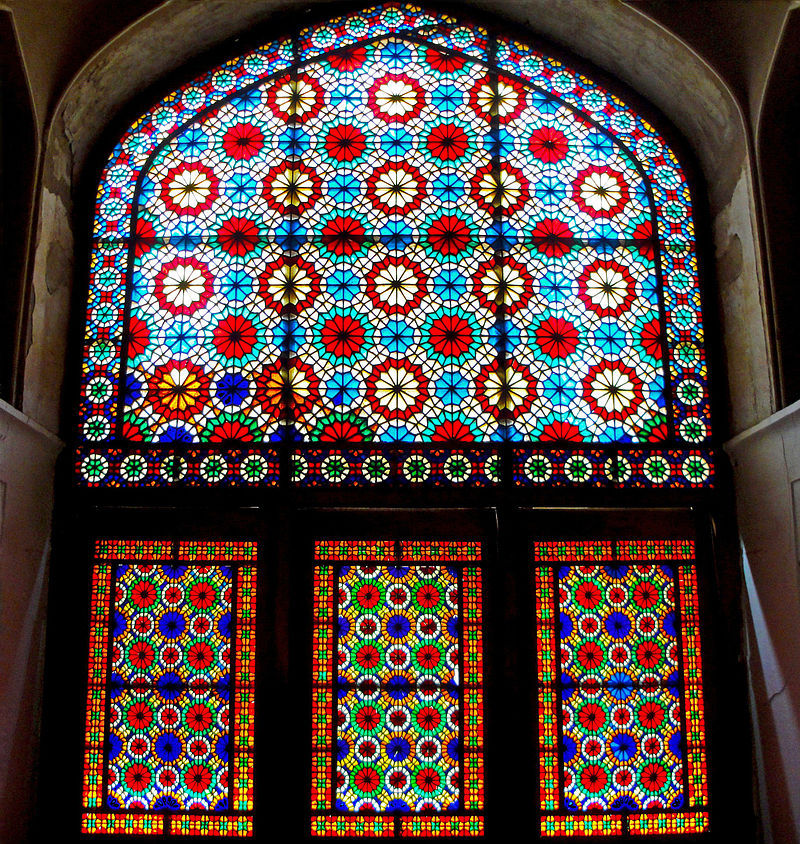

History in Southwest Asia
The creation of stained glass in Southwest Asia began in ancient times. One of the region's earliest surviving formulations for the production of colored glass comes from the Assyrian city of Nineveh, dating to the seventh century BC. The Kitab al-Durra al-Maknuna — attributed to the 8th century alchemist Jābir ibn Hayyān — discusses the production of colored glass in ancient Babylon and Egypt. The Kitab al-Durra al-Maknuna also describes how to create colored glass and artificial gemstones made from high-quality stained glass. The tradition of stained-glass manufacture has continued with mosques, palaces and public spaces being decorated with stained glass throughout the Islamic world. The stained glass of Islam is generally non-pictorial and of purely geometric design but may contain both floral motifs and text.
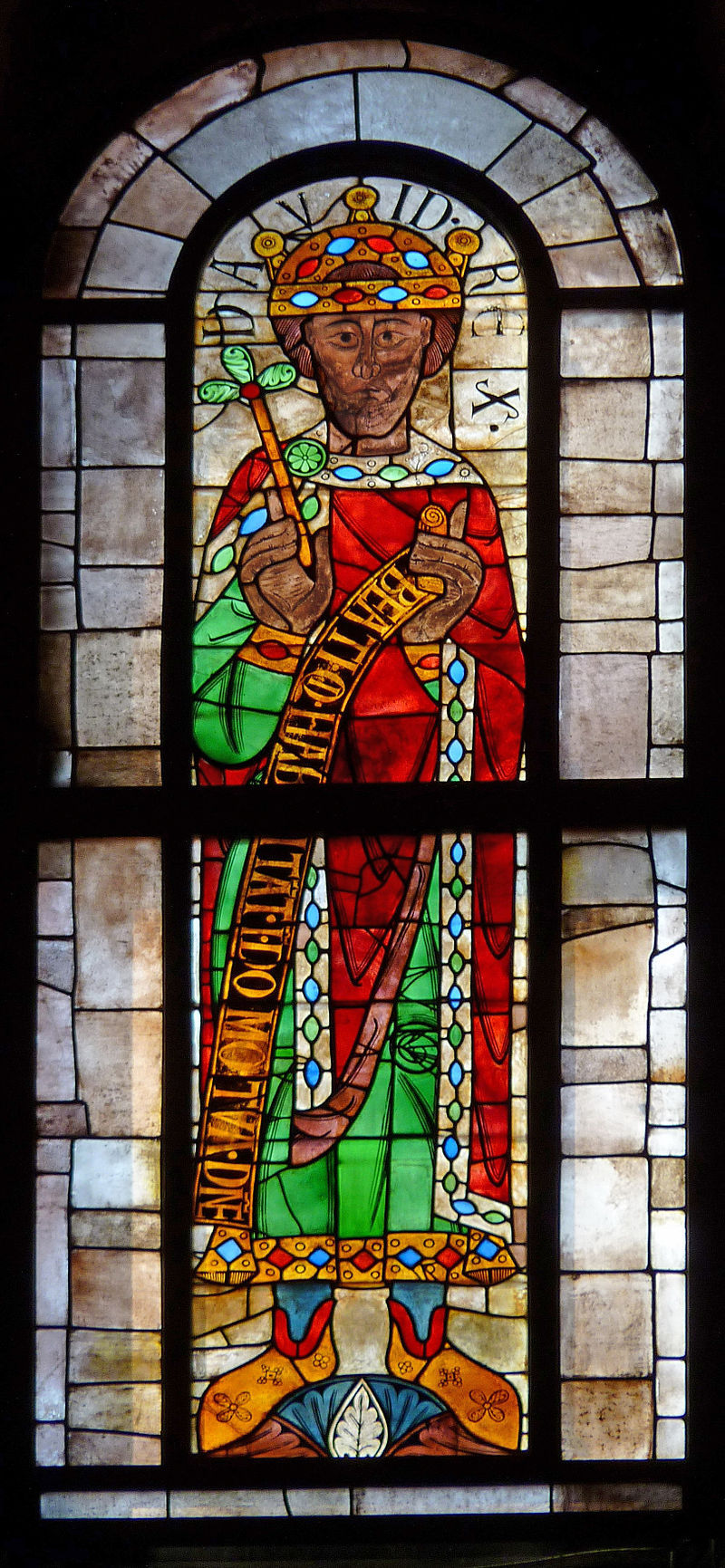

Medieval glass in Europe
Stained glass, as an art form, reached its height in the Middle Ages when it became a major pictorial form used to illustrate the narratives of the Bible to a largely illiterate populace.
In the Romanesque and Early Gothic period, from about 950 to 1240, the untraceried windows demanded large expanses of glass which of necessity were supported by robust iron frames, such as may be seen at Chartres Cathedral and at the eastern end of Canterbury Cathedral. As Gothic architecture developed into a more ornate form, windows grew larger, affording greater illumination to the interiors, but were divided into sections by vertical shafts and tracery of stone. This elaboration of form reached its height of complexity in the Flamboyant style in Europe, and windows grew still larger with the development of the Perpendicular style in England and Rayonnant style in France.
Integrated with the lofty verticals of Gothic cathedrals and parish churches, glass designs became more daring. The circular form or rose window developed in France from relatively simple windows with openings pierced through slabs of thin stone to wheel windows, as exemplified by the west front of Chartres Cathedral, and ultimately to designs of enormous complexity, the tracery being drafted from hundreds of different points, such as those at Sainte-Chapelle, Paris and the "Bishop's Eye" at Lincoln Cathedral.
While stained glass was widely manufactured, Chartres was the greatest center of stained-glass manufacture, producing glass of unrivaled quality.
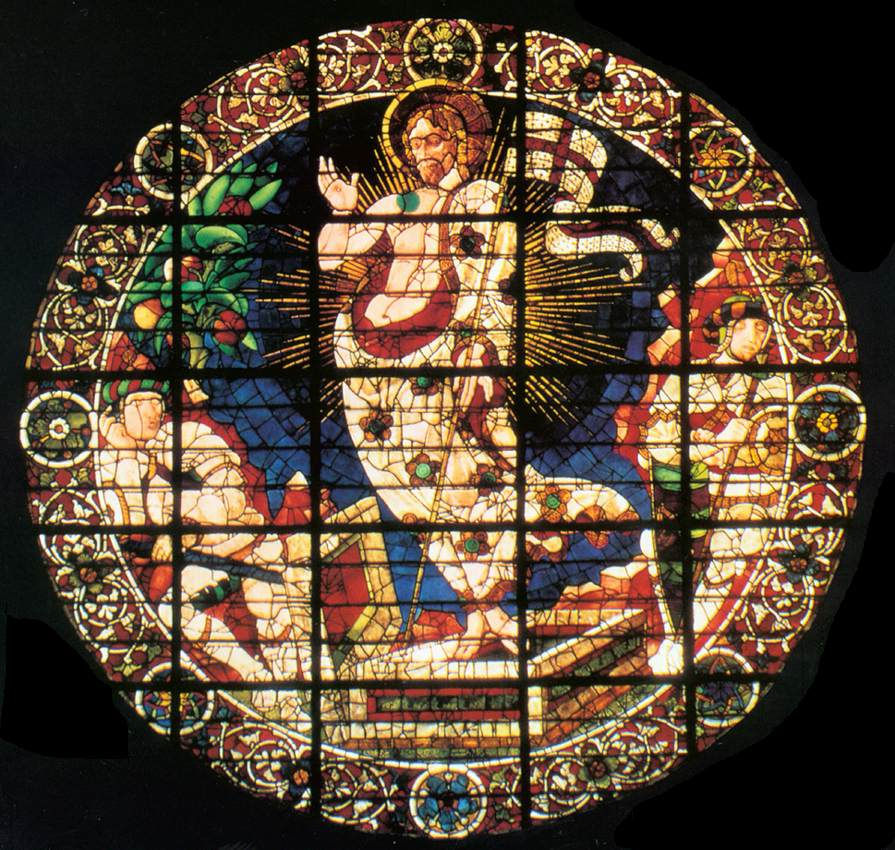

Renaissance, Reformation and Classical windows
Probably the earliest scheme of stained-glass windows that was created during the Renaissance was that for Florence Cathedral, devised by Lorenzo Ghiberti. The scheme includes three ocular windows for the dome and three for the facade which were designed from 1405 to 1445 by several of the most renowned artists of this period: Ghiberti, Donatello, Uccello and Andrea del Castagno. Each major ocular window contains a single picture drawn from the Life of Christ or the Life of the Virgin Mary, surrounded by a wide floral border, with two smaller facade windows by Ghiberti showing the martyred deacons, St Stephen and St Lawrence. One of the cupola windows has since been lost and that by Donatello has lost nearly all of its painted details.
In Europe, stained glass continued to be produced; the style evolved from the Gothic to the Classical, which is well represented in Germany, Belgium and the Netherlands, despite the rise of Protestantism. In France, much glass of this period was produced at the Limoges factory and in Italy at Murano, where stained-glass and faceted lead crystal are often coupled together in the same window. The French Revolution brought about the neglect or destruction of many windows in France.
At the Reformation in England, large numbers of medieval and Renaissance windows were smashed and replaced with plain glass. The Dissolution of the Monasteries under Henry VIII and the injunctions of Thomas Cromwell against "abused images" — the object of veneration — resulted in the loss of thousands of windows. Few remain undamaged; of these the windows in the private chapel at Hengrave Hall in Suffolk are among the finest. With the latter wave of destruction, the traditional methods of working with stained glass died, and were not rediscovered in England until the early 19th century.
In the Netherlands a rare scheme of glass has remained intact at Grote Sint-Jan Church, Gouda. The windows, some of which are 59 feet high, date from 1555 to the early 1600s; the earliest is the work of Dirck Crabeth and his brother Wouter. Many of the original cartoons still exist.
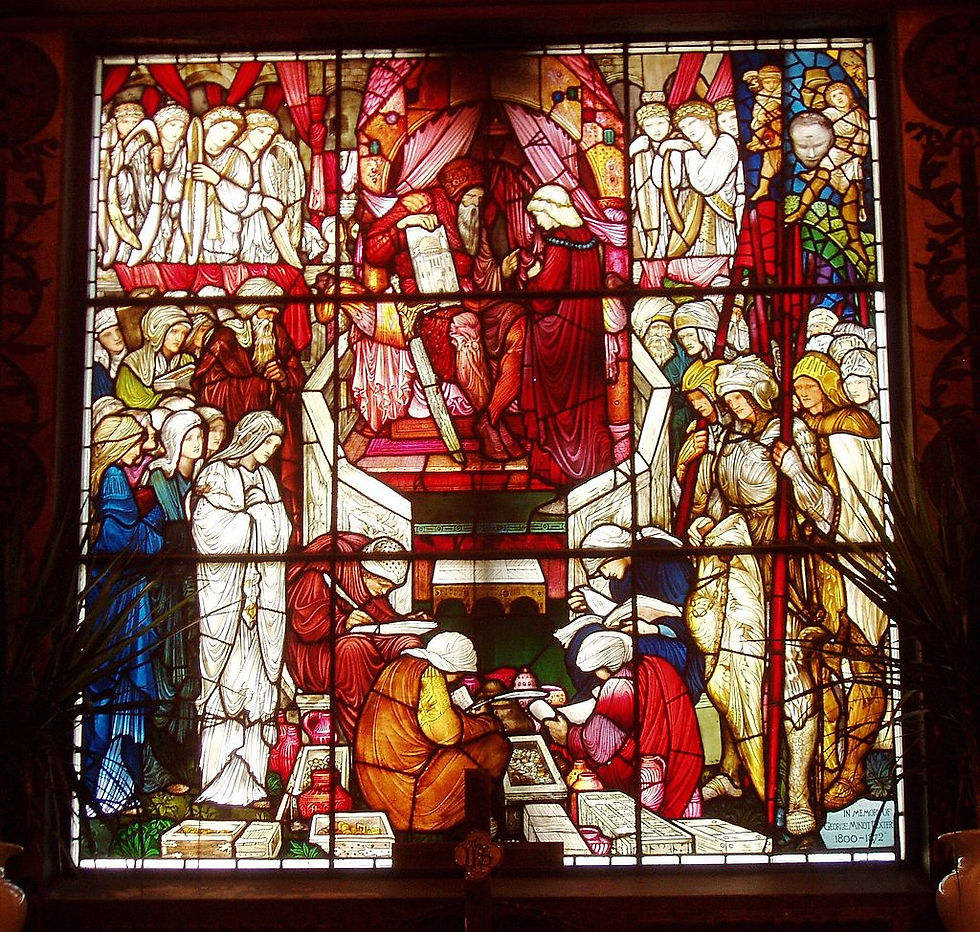

Innovations in Britain and Europe
Among the most innovative English designers were the Pre-Raphaelites, William Morris (1834–1898) and Edward Burne-Jones (1833–1898), whose work heralds the influential Arts & Crafts Movement, which regenerated stained glass throughout the English-speaking world. Among its most important exponents in England was Christopher Whall (1849-1924), author of the classic craft manual “Stained Glass Work,” published London and New York, 1905, who advocated the direct involvement of designers in the making of their windows. His masterpiece is the series of windows (1898-1910) in the Lady Chapel at Gloucester Cathedral. Whall taught at London's Royal College of Art and Central School of Arts and Crafts: his many pupils and followers included Karl Parsons, Mary Lowndes, Henry Payne, Caroline Townshend, Veronica Whall (his daughter) and Paul Woodroffe. The Scottish artist Douglas Strachan (1875-1950) — who was much influenced by Whall's example — developed the Arts & Crafts idiom in an expressionist manner, in which powerful imagery and meticulous technique are masterfully combined. In Ireland, a generation of young artists taught by Whall's pupil Alfred Child at Dublin's Metropolitan School of Art created a distinctive national school of stained glass: its leading representatives were Wilhelmina Geddes, Michael Healy and Harry Clarke.
Art Nouveau or Belle Epoque stained glass design flourished in France and Eastern Europe where it can be identified by the use of curving, sinuous lines in the lead and swirling motifs. In France it is seen in the work of Francis Chigot of Limoges. In Britain it appears in the refined and formal leadlight designs of Charles Rennie Mackintosh.
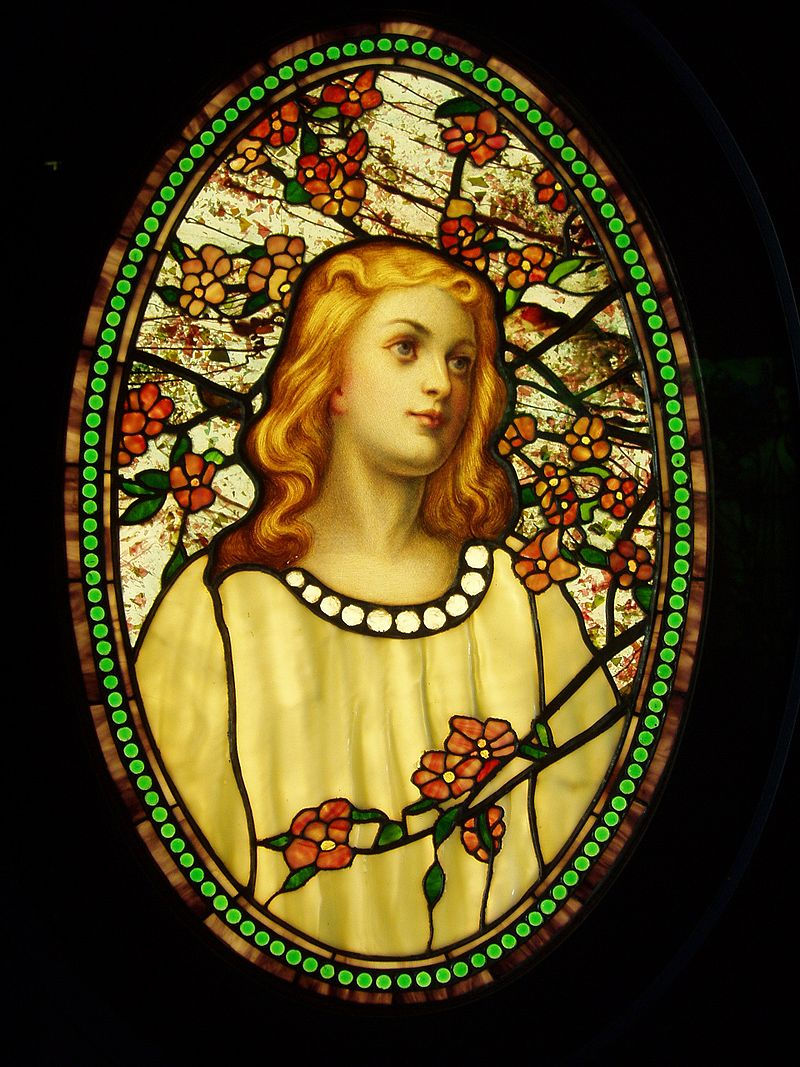

Innovations in the United States
J&R Lamb Studios — established in 1857 in New York City — was the first major decorative arts studio in the United States and for many years a major producer of ecclesiastical stained glass.
Notable American practitioners include John La Farge (1835–1910), who invented opalescent glass and for which he received a U.S. patent on February 24, 1880, and Louis Comfort Tiffany (1848–1933), who received several patents for variations of the same opalescent process in November of the same year, and he used the copper foil method as an alternative to lead in some windows, lamps and other decorations. Sanford Bray of Boston patented the use of copper foil in stained glass in 1886. However, a reaction against the aesthetics and technique of opalescent windows — led initially by architects such as Ralph Adams Cram — led to a rediscovery of traditional stained glass in the early 1900s. Charles J. Connick (1875-1945), who founded his Boston studio in 1913, was profoundly influenced by his study of medieval stained glass in Europe and by the Arts & Crafts philosophy of Englishman Christopher Whall. Connick created hundreds of windows throughout the U.S., including major glazing schemes at Princeton University Chapel (1927-9) and at Pittsburgh's Heinz Memorial Chapel (1937-8). Other American artist-makers who espoused a medieval-inspired idiom included Nicola D'Ascenzo of Philadelphia, Wilbur Burnham and Reynolds, Francis & Rohnstock of Boston and Henry Wynd Young and J. Gordon Guthrie of New York.
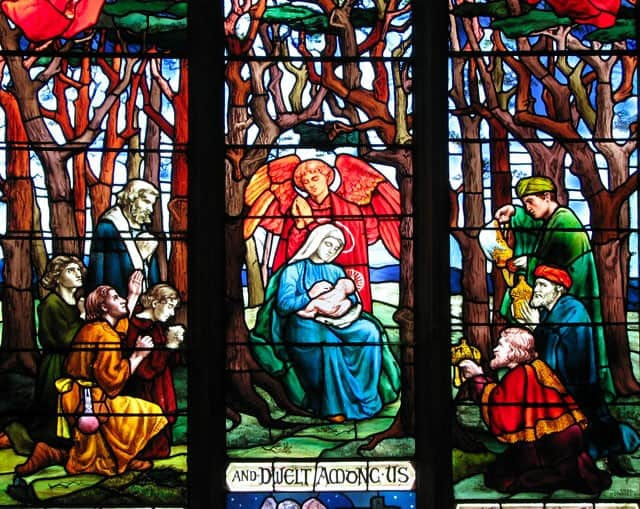

20th and 21st centuries
Many 19th-century firms failed early in the 20th century as the Gothic movement was superseded by newer styles. At the same time, there were also some interesting developments where stained glass artists took studios in shared facilities. Examples include the Glass House in London set up by Mary Lowndes and Alfred J. Drury and An Túr Gloine in Dublin, which was run by Sarah Purser and included artists such as Harry Clarke.
A revival occurred in the middle of the century because of a desire to restore thousands of church windows throughout Europe destroyed as a result of World War II bombing. German artists led the way. Much work of the period is mundane and often was not made by its designers, but industrially produced.
Other artists sought to transform an ancient art form into a contemporary one, sometimes using traditional techniques while exploiting the medium of glass in innovative ways and in combination with different materials. The use of slab glass — a technique known as Dalle de Verre, where the glass is set in concrete or epoxy resin — was a 20th-century innovation credited to Jean Gaudin and brought to the UK by Pierre Fourmaintraux. One of the most prolific glass artists using this technique was the Dominican Friar Dom Charles Norris OSB of Buckfast Abbey.

Gemmail — a technique developed by the French artist Jean Crotti in 1936 and perfected in the 1950s — is a type of stained glass where adjacent pieces of glass are overlapped without using lead cames to join the pieces, allowing for greater diversity and subtlety of color. Many famous works by late 19th- and early 20th-century painters, notably Picasso, have been reproduced in gemmail. A major exponent of this technique is the German artist Walter Womacka.
Among the early well-known 20th-century artists who experimented with stained glass as an abstract art form were Theo van Doesburg and Piet Mondrian. In the 1960s and 1970s the expressionist painter Marc Chagall produced designs for many stained glass windows that are intensely colored and crammed with symbolic details. Important 20th-century stained glass artists include John Hayward, Douglas Strachan, Ervin Bossanyi, Louis Davis, Wilhelmina Geddes, Karl Parsons, John Piper, Patrick Reyntiens, Johannes Schreiter, Brian Clarke and Paul Woodroffe, along with Jean René Bazaine at Saint Séverin; Sergio de Castro at Couvrechef- La Folie (Caen), Hamburg-Dulsberg and Romont, Switzerland; and the Loire Studio of Gabriel Loire at Chartres. The west windows of England's Manchester Cathedral,by Tony Hollaway,are some of the most notable examples of symbolic work.

In Germany, stained glass development continued with the inter-war work of Johan Thorn Prikker and Josef Albers, and the post-war achievements of Joachim Klos, Johannes Schreiter and Ludwig Shaffrath. This group of artists, who advanced the medium through the abandonment of figurative designs and painting on glass in favor of a mix of biomorphic and rigorously geometric abstraction, and the calligraphic non-functional use of leads, are described as having produced "the first authentic school of stained glass since the Middle Ages." The works of Ludwig Schaffrath demonstrate the late 20th-century trends in the use of stained glass for architectural purposes, filling entire walls with colored and textured glass. In the 1970s young British stained-glass artists such as Brian Clarke were influenced by the large scale and abstraction in German 20th-century glass.
After the First World War, stained glass window memorials were a popular choice among wealthier families; examples can be found in churches across the UK.
In the United States, there is a 100-year-old trade organization, The Stained Glass Association of America, whose purpose is to function as a publicly recognized organization to assure survival of the craft by offering guidelines, instruction and training to craftspersons. The SGAA also sees its role as defending and protecting its craft against regulations that might restrict its freedom as an architectural art form. The current president is Kathy Bernard. Today there are academic establishments that teach the traditional skills. One of these is Florida State University's Master Craftsman Program, which recently completed 30-feet high stained-glass windows, designed by Robert Bischoff, the program's director, and Jo Ann, his wife and installed to overlook Bobby Bowden Field at Doak Campbell Stadium. The Roots of Knowledge installation at Utah Valley University in Orem, Utah is 200 feet long and has been compared to those in several European cathedrals, including the Cologne Cathedral in Germany, Sainte-Chapelle in France, and York Minster in England.




Comments